Adversarial
Policies: Attacking Deep Reinforcement Learning
Authors: Adam Gleave, Michael Dennis, Cody Wild, Neel Kant, Sergey
Levine, Stuart Russel at the University of California
Presentation by Group 6: Azin Atarodi, Amaal Ahmed
Summarized by Group 5: Eric Jones, Julian Johnson
Summary
†The presentation consists of using adversarial
policies to attack reinforcement learning. This is applied to a two-player
Markov game using multi-Joint in four different scenarios with different goals,
such as kick and defend, you shall not pass, Sumo, and 2d Sumo. All were
trained with LSTM except You shall not pass which was trained with MLP.† The adversarial policy excelled at the you
shall not pass scenario by confusing the victim by curling up in a ball. This
unexpected behavior caused the adversarial opponent to win 86% of these
scenarios. This demonstrates adversarial policies that can be applied to
robotics.
†
Motivation
In CPS, attackers
can only cause natural but adversarial observations.

Key question
Can an opponent policy systematically make a strong RL agent fail?
Background
Some prior
work focuses on improving robustness and performance in dim settings; however,
this research does not focus on acting in the world, instead of editing
sensors.

Environment
and Victim Policies
To simulate
these policies, the researchers employ Multi-Joint
dynamics with Contact (MuJoCo) where two agents
control humanoid models trained on various MLs.

Threat
Model & Formulation
The
simulation is a two-player Markov game where players attempt to maximize their
sums of rewards, eventually finding an adversarial policy maximizing rewards.

Methods
Evaluated
Optimization
was done with model-free Proximal Policy Optimization.

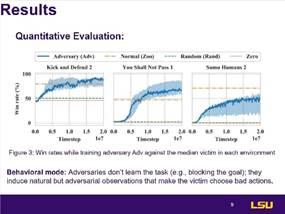
Results
In MuJoCo, the adversarial policy achieved almost two times as
many victories against the victim as the normal opponent.

Understanding
Adversarial Policies
A masked
policy hides the opponent pose in MuJoCo and replaces
it with a static initial position vector, forcing adversarial observations. The
attacker manipulates what the victim sees.
†


Defending
Against Adversarial Polices
On the
defensive side, they employed single fine tuning and dual fine tuning. Using an
adaptive attacker, high win rates were maintained.

Contributions
This paper
used a simulation to show a more realistic and highly successful attack via an adversarial
policy. It showed that these adversarial policies exist and that these attacks
work.

Limitations
Some
limitations include only testing in a simulation, on a fixed victim, testing in
a limited amount of games, and using only a two-agent
setup.

Connection
to course
This
research connects to the course by showing that reinforcement learning and
neural networks can serve as viable attack and defense methods in a cyber
physical system, alongside methods to make use of these tools defensively.

Earlier
Related Work
Szegedy et
al. showed that changing pixels could force a neural network to give completely
wrong output. Goodfellow et al. introduced FGSM and proposed adversarial
training.
Huang et al.
and Pinto et al. incorporated pixel changing to attack RL and physical
disturbances to make an agent stronger instead of weaker.


Follow-up
Research
Follow up research
further tested observation attacks on a reinforcement learning agent and
vulnerabilities of neural networks in reinforcement learning.

Teamwork
The two
cooperated heavily on the presentation, with both reviewing the paper together
and editing to ensure the presentation goes smoothly.

Q&A
1.
What would your idea of the next step be if you were to continue the
research
a.
We can make different opponents with different attacks to learn more on different attacks
2.
On you shall not pass adv wins 87% are all the games in that ballpark
a.
Itís just for one game and itís different for other games sumo has lower
rate of success
3.
How do you find a solution to safeguard an agent from getting worse
instead of getting better on these online
a.
Improve each step by adding more agents, the victims have offline
learning but apply the adversarial learned through the game, most are learned
offline. If they tried to do it online the environment will
be more complex. The victim might have some unstable solutions
b.
Pos sol for maintaining safety
i.
Add more sensors to make decisions
ii.
How can a sensor determine if the agent can learn something or not learn
something

Discussion
1.How can
we improve the robustness of reinforcement learning agents against natural
adversarial behaviors?
††††††††††† The tuning of the hyper parameters
of the RL and how to get the optimal learning rate mostly through trial and
error if you can find the optimal
††††††††††† Implementing prediction of enemy
moves
†††††††††††
2.How can
simulation results like this be tested or transferred to real robots safely?
††††††††††† Looking at you shall not pass game
if it had an estimated state vector confused limb for limb, use most safe
option
†††††††††††
3.Instead
of training stronger agents, could we design environments or rules that
naturally prevent adversarial behaviors?
††††††††††† Designing environments is not easy,
you can improve policy. On policy training method that can learn
the environment no matter complex, training would take
much more time
If we
tried to make game, all agents work together to cooperate

